Hybrid VM Management with Azure Arc-enabled System Center VMM
As customers continue to leverage Microsoft Azure to build, deploy, and manage business critical applications at scale, hybrid cloud is quickly becoming their mainstay. Customers have been telling us that a consistent experience of managing and securing their diverse IT environments will be key as they scale their cloud-native applications and infrastructure.
To enable the flexibility and agility customers are seeking, we introduced Azure Arc – a set of technologies that extends the Azure platform so you can build applications and services with the flexibility to run across datacenters, edge, and multicloud environments.
Azure Arc enables customers to secure and govern their physical or virtual infrastructure and Kubernetes clusters anywhere using familiar Azure Management practices. Customers can also build cloud-native applications with Azure application services and Azure data services on their existing infrastructure in their datacenters, at the edge or in multicloud environments.
Today, our customers use System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) at scale to manage and operate hundreds of physical Servers and tens of thousands of virtual machines on-premises, along with their Azure deployments. We want to ensure that these workloads can also benefit from ongoing innovations in Azure.
Extending Azure Arc to System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM)
Azure Arc-enabled System Center VMM is a new Azure Arc capability, now available in Preview. This enables on-premises System Center VMM environments to be connected to Azure, unlocking Azure-based self-service for end users and developers.
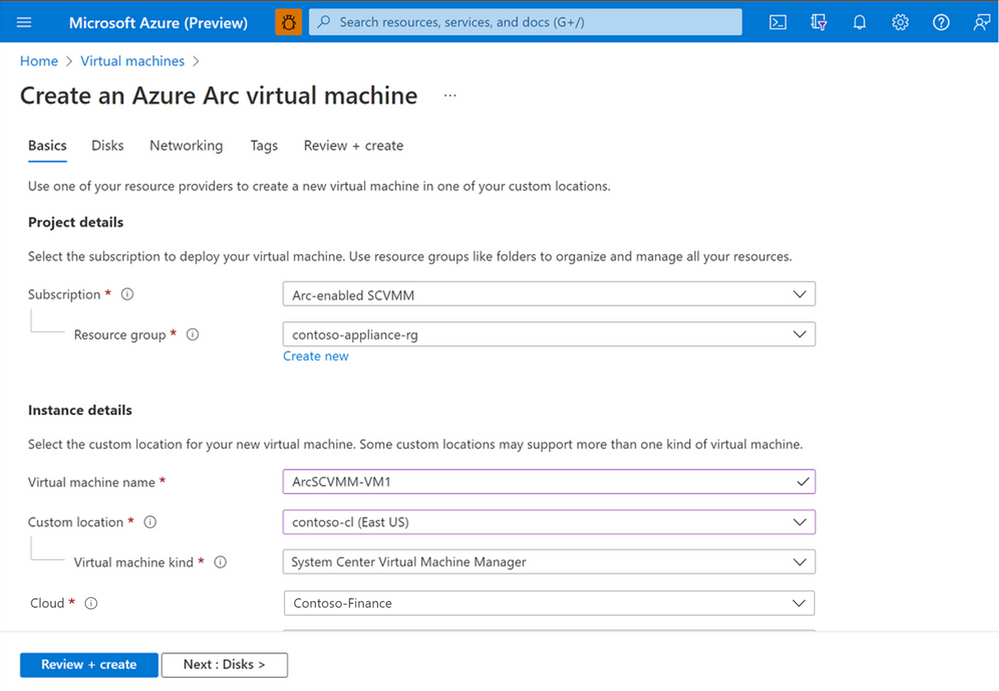
With this, Virtual Machines can now be created, managed and deleted in System Center VMM deployments on-premises through familiar Azure Portal experiences. In addition, end users will be able to deploy and manage VMs in SCVMM using ARM templates, ensuring that they can deploy Infrastructure as Code consistently across Azure and on-premises environments. With ARM templates, DevOps teams can also use CI/CD pipelines to provision or update the VMs along with application updates.
With this integration, IT administrators can now extend the Azure Portal to provide the end users and developers with a familiar and consistent Self-service experience to their VMs and associated resources similar to Azure. In addition, administrators can govern and drive compliance through the rich Azure governance controls and Azure RBAC for the self-service users.
Onboarding SCVMM to Azure Arc:
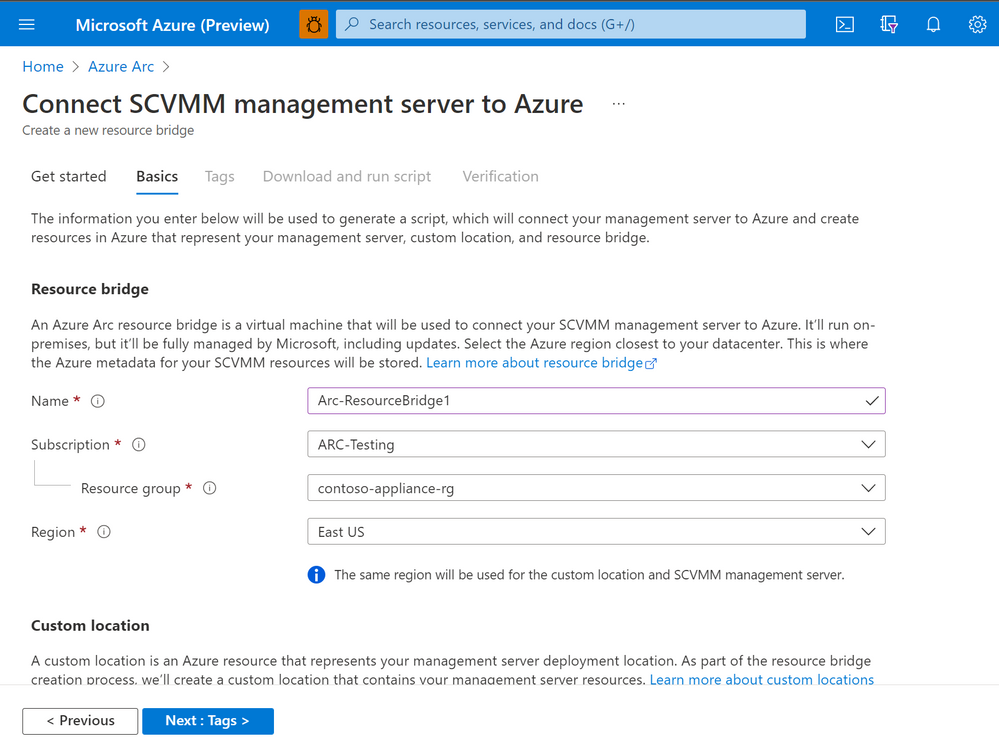
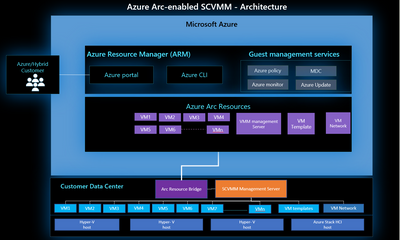
To onboard SCVMM to Azure Arc, administrators would require deploying a virtual appliance called the Arc Resource Bridge. The Arc resource Bridge acts as a gateway connecting the System Center Virtual Machine Manager and Azure. The Resource Bridge hosts the necessary agents and extensions required to communicate to Azure and provide the required representation of the SCVMM resources on Azure.
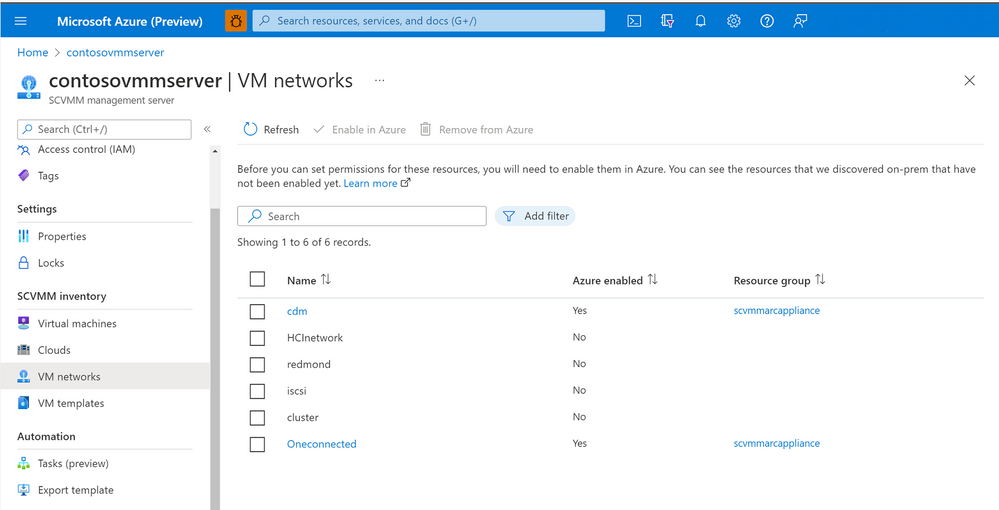
Once the Resource Bridge is operational and connected to Azure, the SCVMM Management Server, the Virtual Machines, VM Networks and other resources are represented and visible in Azure Arc and can be used by customers for operations on their VM and managing their lifecycle.
Get started now
We are very excited to have you try Arc-enabled SCVMM and its capabilities. Please signup here if you would like to receive further updates on Arc-enabled SCVMM.
More information on onboarding and using Arc-enabled SCVMM can be found below:
Overview of Azure Arc-enabled System Center VMM
Connect an SCVMM Management Server to Azure Arc
Create a virtual machine on SCVMM from Azure Arc
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Power Pages + Azure AD B2C: “The Provided Application Is Not Valid” Error
If you are new to configuring Azure AD B2C as Identity Provider in Power Pages, refer Power Pages : Set up Azure AD B2C After completing the s...
Semantic Reranking with Azure SQL, SQL Server 2025 and Cohere Rerank models
Supporting re‑ranking has been one of the most common requests lately. While not always essential, it can be a valuable addition to a solution...
How Azure Cosmos DB Powers ARM’s Federated Future: Scaling for the Next Billion Requests
The Cloud at Hyperscale: ARM’s Mission and Growth Azure Resource Manager (ARM) is the backbone of Azure’s resource provisioning and management...
Automating Business PDFs Using Azure Document Intelligence and Power Automate
In today’s data-driven enterprises, critical business information often arrives in the form of PDFs—bank statements, invoices, policy document...
Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions Enhancements, Foundry Rebranding, and Azure Pipelines Improvements
This post announces the December release of the Azure Developer CLI (`azd`). The post Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions En...
Unlock the power of distributed graph databases with JanusGraph and Azure Apache Cassandra
Connecting the Dots: How Graph Databases Drive Innovation In today’s data-rich world, organizations face challenges that go beyond simple tabl...
Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot
A few months ago we introduced the Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot in private preview. The goal was simple: allow teams to take a...