Virtual Wan Traffic Flow Patterns
Virtual Wan Traffic Flow Scenarios
This guide offers an exploration of the essential elements related to vWAN traffic flows, including their significance in shaping flow topology patterns. At the heart of the vWAN branch architecture lie pivotal components such as VPN, SD-WAN, and ExpressRoute. Within the vHub ecosystem, the routing instances hold the crucial role in managing traffic flows, employing BGP for communication. These routing instances, concealed from the end user within the vHub, serve as the linchpin of the vWAN system. The routing instances bear the responsibility of intercepting and directing traffic flows, ensuring the smooth transmission of data packets. If packet flow inspection is also required, these can be aided by an Azure Firewall (AzFW) or Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) inside the vHub. The moment an NVA or AzFW is incorporated into the vHub, they gain control over the data plane packet interception. To enable this inspection, Routing Intent must be enabled on multi-vhub scenarios, or Private/Internet Traffic must be enabled via Firewall policy if an Azure Firewall is deployed within the vHub(s). The subsequent diagrams offer a pictorial depiction of the various flow patterns observed for single and multiple hubs within the vWAN infrastructure. The intent of this article is to provide a more detailed depiction of flow patterns than currently available in the Azure public documents, vWAN Flow Patterns. Understanding the flows and components involved in vWAN pricing is also essential, and this can help explain how vWAN pricing works. For details on vWAN pricing, please refer to the vWAN Pricing Page
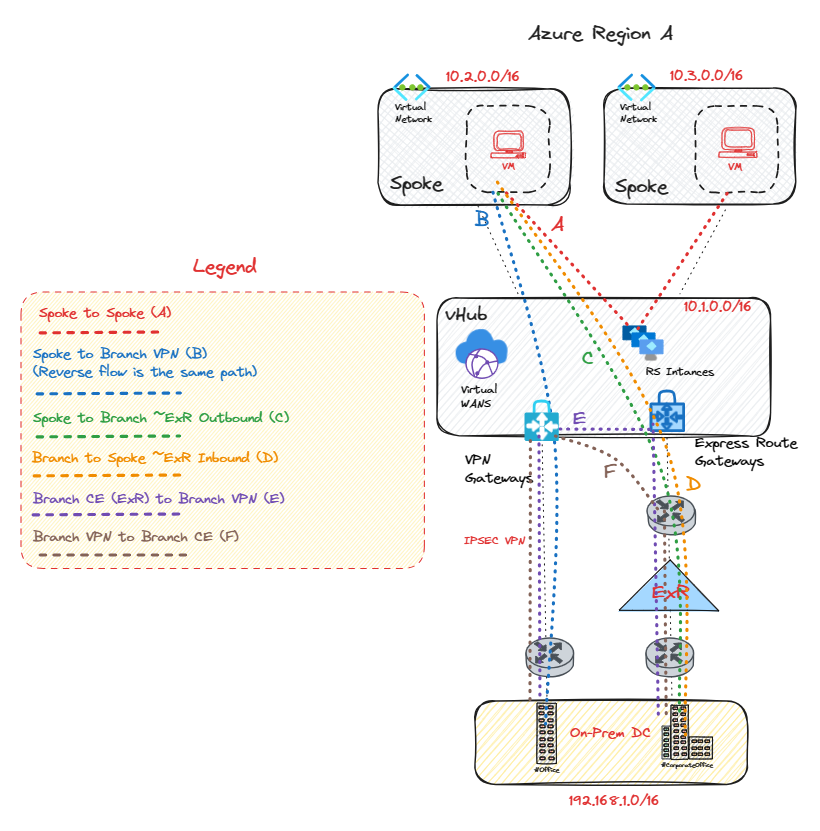
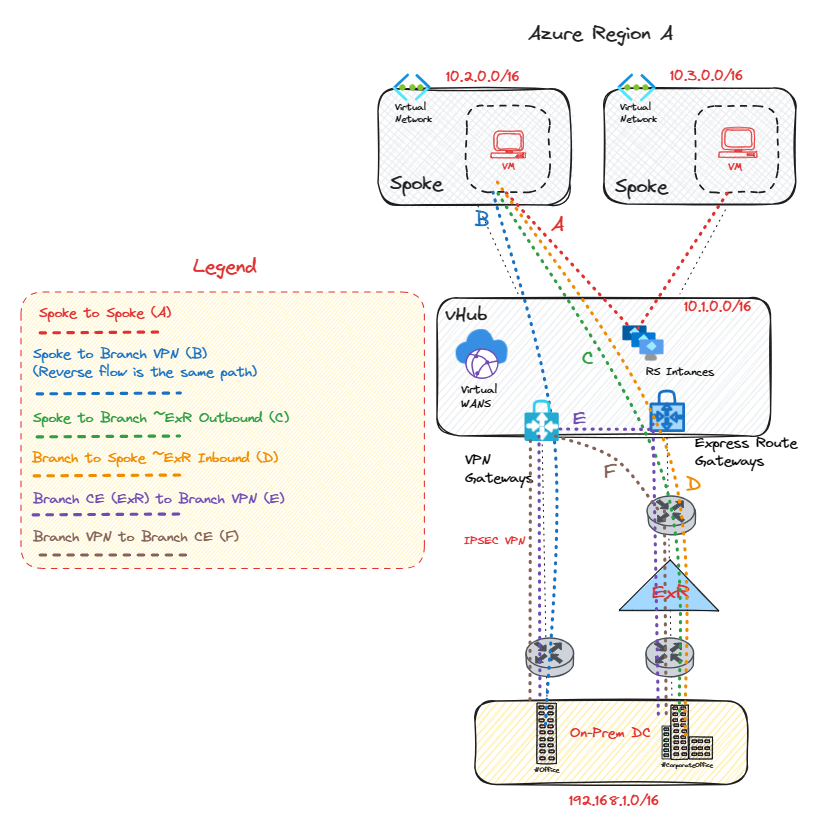
Single vWAN Hub
| Traffic Flows | Traffic Flow Paths |
|---|---|
| Flow A | Spoke VM-->Routing Instances-->Spoke VM |
| Flow B | Spoke VM-->vHub VPN-->Branch VPN Concentrator |
| Flow C | Spoke VM-->MSEE IP-->Branch Customer Edge (CE) (Egress flows for ExR bypass the ExR GW!) |
| Flow D | Branch Customer Edge (CE)-->MSEE IP-->ExpressRoute GW-->Spoke VM |
| Flow E | Branch Customer Edge (CE)-->MSEE IP-->ExpressRoute GW-->vHub VPN Gateway-->Branch VPN Concentrator |
| Flow F | Branch VPN Concentrator-->vHub VPN--->MSEE IP-->Branch Customer Edge (CE) (Egress flows for ExR bypass the ExR GW!) |
Quick Take-Aways
In the aforementioned flow paths, it's pertinent to note that the Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be substituted with a Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) tunnels to yield identical results in the diagram above. If either an Azure Firewall or Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) is deployed within the virtual hub (vHub), they will intercept packets in lieu of the route service's Virtual IP (VIP), granted that Routing Intent is activated, or Private/Internet security via Azure Firewall policy on a single vHub!
During operations within a single vHub, it's important to realize that flows to and from branches, whether via IPSEC, SD-WAN, or ExpressRoute, do not traverse the route service instances. Instead, this pattern is only observed in Spoke to Spoke flows, which contributes towards the vHub infrastructure limit, currently capped at 50Gbps per vHub, For additional details, please refer to the linked resource. Lastly, it should be mentioned that Branch to Branch flows also bypass the route service instances.
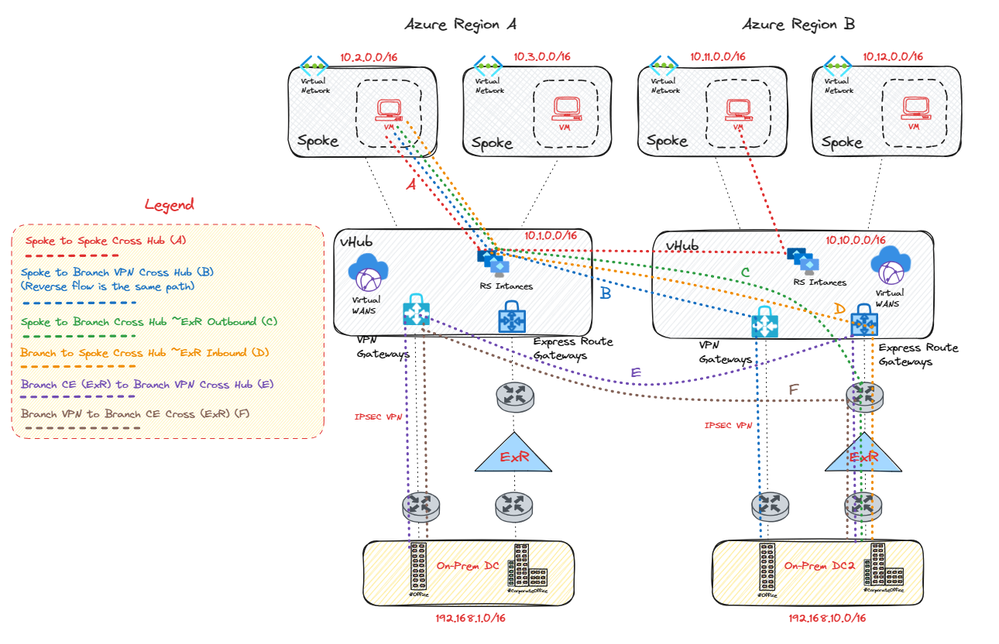
Multiple vWAN Hubs
| Traffic Flows | Traffic Flow Paths |
|---|---|
| Flow A | Spoke VM-->Routing Instances-->Remote Routing Instances-->Remote Spoke VM |
| Flow B | Spoke VM-->Routing Instances--->Remote vhub VPN-->Remote Branch VPN Concentrator |
| Flow C | Spoke VM-->Routing Instances-->Remote MSEE IP--->Remote Branch Customer Edge (CE) (Egress flows for ExR bypass the ExR GW!) |
| Flow D | Branch Customer Edge (CE)-->MSEE IP-->ExpressRoute GW-->Remote Routing Instances-->Remote Spoke VM |
| Flow E | Branch Customer Edge (CE)-->MSEE IP-->ExpressRoute GW-->Remote vHub VPN GW-->Remote Branch VPN Concentrator |
| Flow F | Branch VPN Concentrator-->Remote MSEE IP-->Remote Branch Customer Edge (CE) (Egress flows for ExR bypass the ExR GW!) |
The same principles apply to multiple vHubs in terms of SD-WAN tunnels and Azure Firewall/NVA behavior as they do a single vHub.
In the flow patterns for multiple vHubs, we note that Spoke-to-Spoke communication across hubs invariably involves the routing instances. Traffic moving from Spoke to Branch and vice versa also traverses a single set of routing instances. However, Branch-to-Branch traffic does not pass through the routing instances, just like single vHub behavior.
Note:
It's important to acknowledge that Azure Virtual WAN does not natively provide transit for ExpressRoute-to-ExpressRoute flows. To facilitate this, Global Reach is required. For Global Reach details, please refer to the linked resource. Alternatively, an Azure Firewall or NVA can be deployed in each vHub, combined with activation of routing intent and engagement with Microsoft Support. Information on Routing Intent can be found here to facilitate transit between ExR Circuits. Under this configuration, we effectively push down RFC1918 prefixes to each ExpressRoute branch, thereby providing a supernet of transit connectivity.
I hoped this guide helped shed more light on the comprehension of packet flow dynamics within the services employed in vWAN. Armed with this understanding, users are enabled to make informed decisions regarding the infrastructure units, in terms of (Gbps), that should be allocated to each respective vHub, and also the size of their branch gateways (VPN/ExpressRoute) and SD-WAN devices.
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
How to restrict Unwanted Power Automate flow execution
In Microsoft Dataverse, Power Automate flows are commonly used to execute business logic when records are created, updated, or deleted. They w...
Convert CSV files to JSON in Power Automate
How do you convert CSV files to JSON? When you have data in CSV format and you want to use this within Power Automate, there used to be a lot...
3 reasons to use the new designer in Power Automate
Hardly ever, I've seen a software change take so long for people to accept. How long will it be before developers just get on with as the new ...
Power Automate – View property value expanded inline in the new cloud flow designer
We are announcing the ability to view property value expanded inline in the new cloud flow designer in Power Automate. This feature will reach...
Substring vs Slice in Power Automate
Power Automate has quite a few string functions that can help you sort out textual issue. Two of these functions are Substring and Slice. Do y...
Power Automate – Debug easily into condition actions at runtime
We are announcing the ability to debug condition actions by displaying values passed into the dynamic content and expressions at runtime in Po...
Run a generative action in Power Automate
Recently the Run a generative action was added to Power Automate. To make this action work is not as easy as you might hope.
Send community news by email using Power Automate
Yesterday on Reddit I was asked about how to collect and send community news articles from websites using Power Automate so that news letters ...
4 ways to filter data in Power Automate
Yesterday, I looked at how to filter data when making an API call using the HTTP action and noticed that filtering data isn't always straight ...