Azure Landing Zones Accelerators for Bicep and Terraform. Announcing General Availability!
The Azure Landing Zones team is delighted to announce the general availability of our Azure Landing Zones Accelerators for Bicep and Terraform, having both reached the version 1.0 milestone. This article will provide an overview of the accelerators and dive into the common approaches for deploying them.
We'll cover:
- What is an Azure Landing Zone?
- What are the Azure Landing Zones Accelerators?
- Why should you use an Accelerator?
- How do you use the Accelerator?
- What does the Bicep Accelerator deploy and configure?
- What does the Terraform Accelerator deploy and configure?
- Where can you learn more?
- Thank you to our collaborators!
What is an Azure Landing Zone?
An Azure Landing Zone serves as the cornerstone of your cloud adoption, establishing guardrails and facilitating the deployment of workloads into Azure in a secure, standardized, and scalable manner. Further details can be found in our Cloud Adtion Framework documentation under: What is an Azure landing zone?
For the purpose of this article, you can consider the landing zone to consist of the initial setup of:
- Management groups
- Azure RBAC Roles
- Azure Policy
- Management resources, such as centralized logging and automation accounts
- Hub networking, Azure DNS, and other connectivity resources
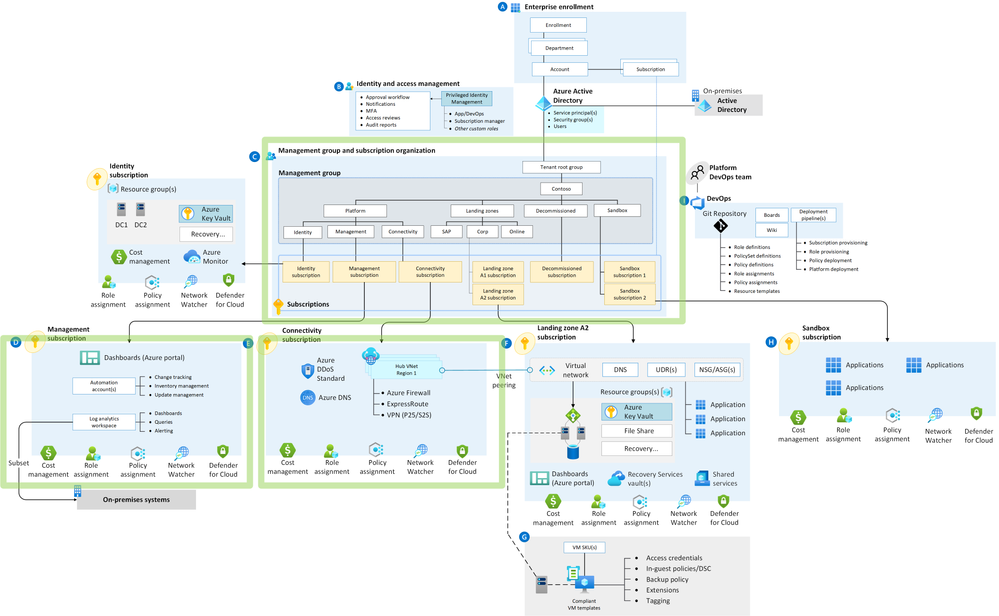
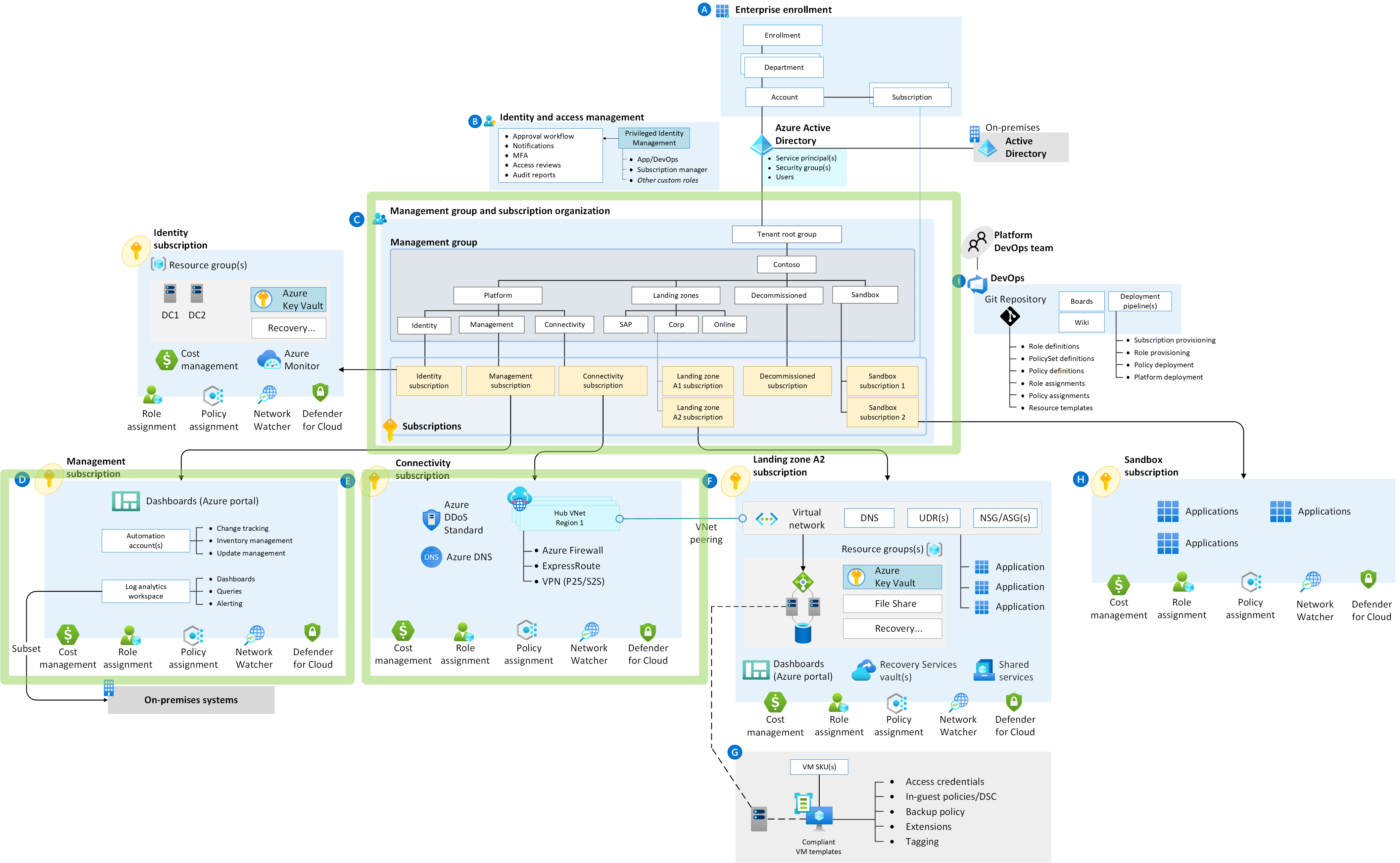
See the green boxes in this diagram:
Figure: Azure Landing Zones Accelerator Scope
What are the Azure Landing Zones Accelerators?
The Azure Landing Zones Accelerators for Bicep and Terraform serve as automation frameworks and include corresponding documentation. Their purpose is to assist our customers and partners in swiftly deploying their Azure Landing Zone architecture by utilizing our pre-existing Azure Landing Zones Bicep or Terraform modules and adhering to best practices. While these accelerators are crafted to meet the requirements of 90% of users by default, they can be tailored to accommodate the specific needs of advanced scenarios.
The Accelerators follow a three phase approach:
- Pre-requisites: Instructions to configure credentials and subscriptions.
- Bootstrap: Automation or instructions to bootstrap managed IaC modules into Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery Pipelines.
- Run: Trigger the pipelines to deploy the Azure Landing Zone architecture.
The Accelerators offer support for utilizing GitHub or Azure DevOps as targets for the bootstrapping automation.
Why should you use an Accelerator?
The Azure Landing Zones Accelerators for Bicep and Terraform play a crucial role in minimizing the effort needed for analyzing and creating an Azure Landing Zone deployment. They offer opinionated patterns and comprehensive automation for setting up Azure Landing Zones modules, ensuring a production-ready configuration.
Before the Accelerators were available, teams invested considerable time constructing their automation for our Azure Landing Zones modules and making decisions regarding the configuration and security of Continuous Delivery. The Accelerators eliminate this overhead by offering a reusable deployment pattern.
How do you use the Accelerator?
The Accelerators wikis provide comprehensive documentation and quick start guides for using the Accelerators. These can be found here:
The Accelerators use a shared approach to the bootstrapping process with a common PowerShell module. The ALZ PowerShell module is available from the PowerShell Gallery.
The basic PowerShell to bootstrap GitHub or Azure DevOps is:
What does the Bicep Accelerator deploy and configure?
The Azure Landing Zone Bicep Accelerator comes with a comprehensive set of instructions to guide you through the provisioning process. It assists in selecting options that are relevant to your needs and prompts you for choices within the PowerShell automation.
The Bicep Accelerator offers flexibility, allowing you to determine how you want to secure your repositories and pipelines/actions. While we provide guidance and examples, you have the freedom to choose the type of authentication that GitHub or Azure DevOps employs.
Details of what is deployed by following the Accelerator steps:
- Microsoft Azure
- Deployment identity
- Version Control System (GitHub or Azure DevOps)
-
Repositories and files
-
Azure Pipelines/GitHub Workflows
- Environment Variables
- Branch Policies
-
The Azure Pipelines and GitHub Workflows leverage PowerShell scripts for deploying the modules, and their structure is illustrated in the following diagram:
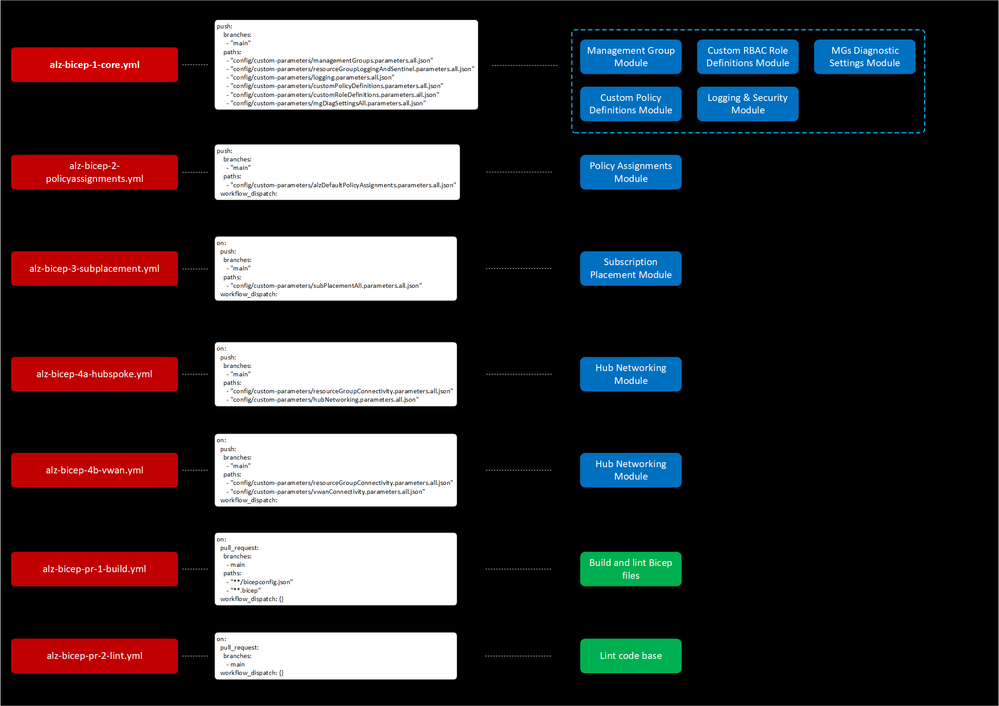
Additionally, we provide prescription documentation for managing specific scenarios:
- Handling upgrades to newer versions of ALZ-Bicep.
- An opinionated approach to introducing a branching strategy into your CI/CD process.
- Process for incorporating modified ALZ-Bicep Modules into the Accelerator framework.
Ultimately, the documentation comprehensively guides the setup of Azure DevOps/GitHub, encompassing the configuration of the repository, pipelines, and branch policies. Furthermore, there are intentions to implement automation to streamline and reduce manual efforts. Stay tuned for future updates on this blog post as we finalize and incorporate these enhancements!
What does the Terraform Accelerator deploy and configure?
The Azure Landing Zones Terraform Accelerator has many options to choose from when deploying the bootstrap. You can use variables to choose between the options shown in the table below. Our default options are shown in green text, as these provide the highest level of security and leverage best practice authentication.
| Version Control System | Agents / Runners | Networking | Authentication |
| GitHub | Microsoft Hosted | Public | Workload identity federation |
| GitHub | Self Hosted | Public | Workload identity federation |
| GitHub | Self Hosted | Private | Workload identity federation |
| Azure DevOps | Microsoft Hosted | Public | Workload identity federation |
| Azure DevOps | Self Hosted | Public | Workload identity federation |
| Azure DevOps | Self Hosted | Private | Workload identity federation |
| Azure DevOps | Self Hosted | Public | Managed identity |
| Azure DevOps | Self Hosted | Private | Managed identity |
The Terraform Accelerator follows the 3 phase approach as described previously:

Details of what is deployed by the bootstrap can be found in our documentation, but in summary the bootstrap will deploy:
- Microsoft Azure
- Storage
- Identity
- Networking
- Self-hosted Agents / Runners
- Version Control System (GitHub or Azure DevOps)
- Repositories and files
- Pipelines / Actions
- Environments
- Approvals
- Branch Policies
- Variables

Where can you learn more?
Thank you to our collaborators
We express our heartfelt gratitude to everyone who collaborated on the Azure Landing Zones Accelerators. The tremendous support from individuals involved in testing, offering feedback, contributing code, documentation, and ideas has been invaluable. Thank you for your dedication and contributions to the success of the Accelerators.
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
March Patches for Azure DevOps Server
We are releasing patches for our self‑hosted product, Azure DevOps Server. We strongly recommend that all customers stay on the latest, most s...
Azure Developer CLI (azd): Debug hosted AI agents from your terminal
New azd ai agent show and monitor commands help you diagnose hosted AI agent failures directly from the CLI. The post Azure Developer CLI (azd...
A Look Ahead at Azure Cosmos DB Conf 2026: From AI Agents to Global Scale
Join us for Azure Cosmos DB Conf 2026, a free global, virtual developer event focused on building modern applications with Azure Cosmos DB. Da...
Announcing general availability of Azure Confidential Computing (ACC) virtual machines for U.S. government environments
Government agencies have an increased need for secure, verifiable, and compliant cloud environments that adhere to data sovereignty regulation...
What is Azure SRE Agent
Azure Developer CLI (azd): One command to swap Azure App Service slots
The new azd appservice swap command makes deployment slot swaps fast and intuitive. The post Azure Developer CLI (azd): One command to swap Az...