Announcing landing zone accelerator for Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO)
We are excited to announce the General Availability (GA) of the Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) landing zone accelerator within the Cloud Adoption Framework. Landing zone accelerators provide architectural guidance, reference architecture, reference implementations and automation packaged to deploy workload platforms in Azure at scale and aligned with industry proven practices. Like other Landing zone accelerators, the ARO guide delivers resources that help design, deploy, and maintain well Architected ARO platforms. These resources include:
- ARO landing zone accelerator documentation
- ARO landing zone accelerator reference implementation
Documentation
The ARO landing zone accelerator documentation provides a conceptual architecture that can be a great starting point for ARO workloads. Understanding that most workloads are managed by a cross functional team, this modular approach by critical design areas such as security, management, network topology etc. allows a separation of concern so that various teams can focus on the area of the workload platform that they are responsible for. The documentation was developed by a team of subject matter experts with extensive experience building solutions on ARO for themselves and Azure customers.
Reference Implementation
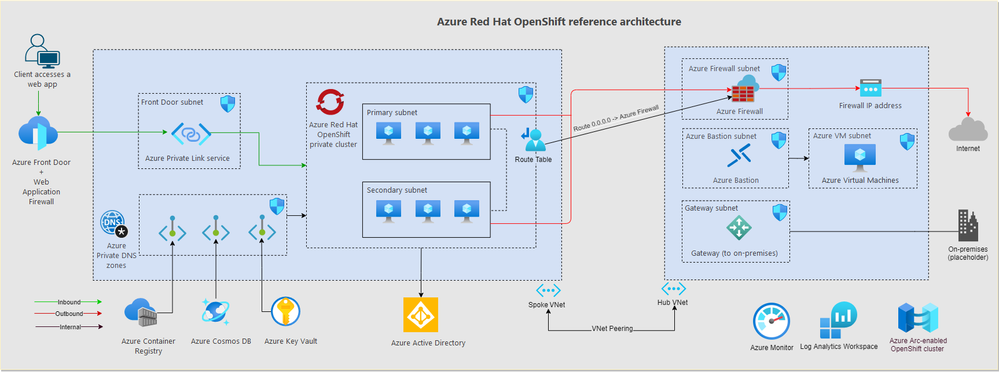
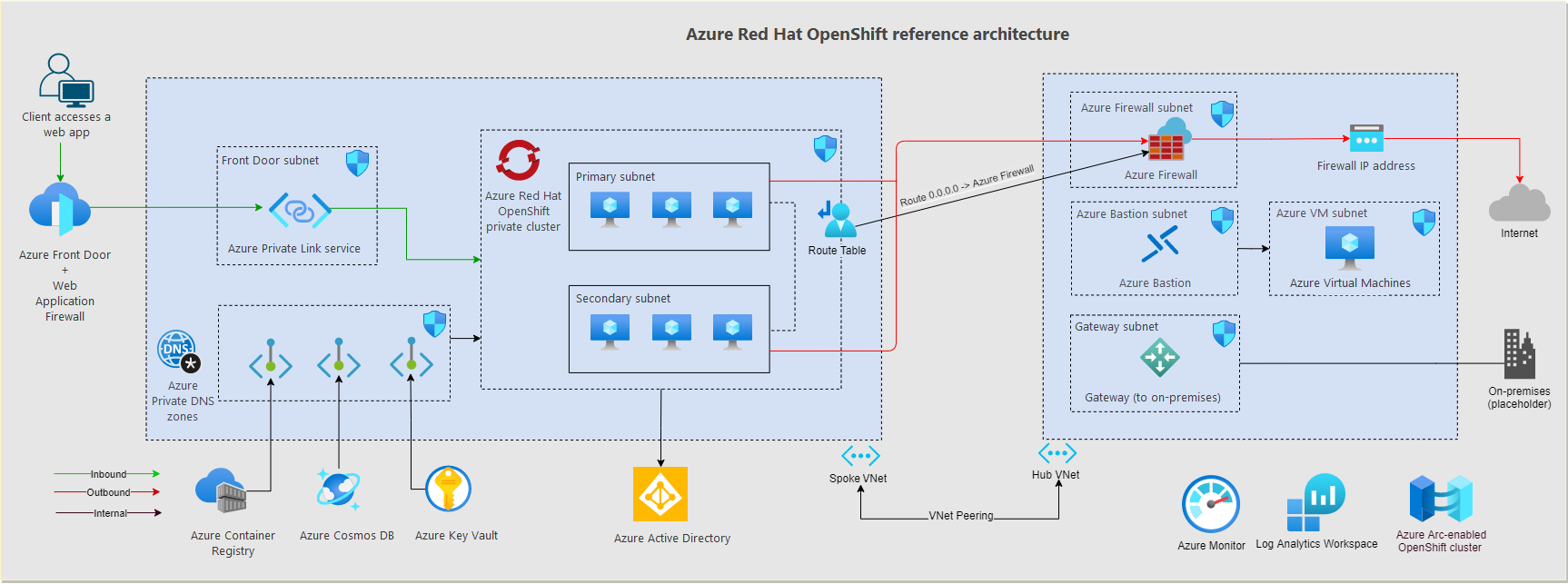
The reference implementation, hosted on GitHub, builds on the documentation, and provides step by step approaches to deploy secure ARO workload platforms. Users of the reference implementation can follow modularized steps which can be customized to fit their specific needs as they are designed to be easily extensible. As of the time of its launch, the ARO secure baseline is available with the deployment options being Azure CLI and Terraform. Below is the reference implementation’s architecture:
Sample scenario
The application development team you work with has decided to migrate their existing application hosted on Red Hat OpenShift virtual machines from on premises to the cloud. The main reasons for this migration are to improve scalability, eliminate the cost and complexity of maintaining physical servers themselves, provide a better service experience to their customers in different continents and take advantage of the agility that comes with building cloud native applications using container technologies. The operations team has been learning the basics of public clouds, containers and Kubernetes and are confident that they can manage Kubernetes infrastructure on the cloud. After reviewing various options, they have decided to migrate their existing workload to Azure Red Hat OpenShift and need guidance on the best way to get started.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift provides highly available, fully managed OpenShift clusters on demand, monitored and operated jointly by Microsoft and Red Hat. OpenShift brings added-value features to complement Kubernetes, making it a turnkey container platform as a service (PaaS) with a significantly improved developer and operator experience. As a solution architect, you’ll need to consider the ARO operator’s role of providing a cost effective yet scalable and secure platform for your development team.
Using the self-service solution that is the ARO landing zone accelerator, you can learn some of the important architectural considerations and recommendations that need to be decided upon to ensure you are deploying your ARO platform the right way. You can explore the critical design areas and make important decisions based on the guidance. When it is time for deployment, you don’t have to start from scratch. Instead, you have ready to deploy Terraform templates as well as Azure CLI deployment steps that can significantly speed up your journey to production. You add a backlog item to periodically revisit the guidance to make sure your site's workload platform is incorporating any new recommendations and to evaluate any architectural changes made to the platform since it was last reviewed, knowing the landing zone accelerator will continue to evolve with ARO.
Getting started
Head over to the ARO landing zone accelerator page and explore the landing zone accelerator, the critical design areas, and reference implementation.
Related Azure landing zone accelerators
If you are looking for more structured guidance around Azure’s modern application platforms like ARO, check out the other landing zone accelerators available:
- AKS landing zone accelerator for similar best practices on Azure Kubernetes Services
- App Service landing zone accelerator for similar best practices on App Service Environment v3
- APIM landing zone accelerator for similar best practices for preparing scalable API management infrastructure on APIM
Author Bio
Ayobami Ayodeji is a Senior Program Manager who leads teams that create technical assets to support architecture guidance around Azure’s container related services. He also leads the architecture review board for container workloads in Azure Architecture Center.
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Microsoft Purview: Data Lifecycle Management- Azure PST Import
Azure PST Import is a migration method that enables PST files stored in Azure Blob Storage to be imported directly into Exchange Online mailbo...
How Snowflake scales with Azure IaaS
Microsoft Rewards: Retirement of Azure AD Account Linking
Microsoft is retiring the Azure AD Account Linking feature for Microsoft Rewards by March 19, 2026. Users can no longer link work accounts to ...
Azure Function to scrape Yahoo data and store it in SharePoint
A couple of weeks ago, I learned about an AI Agent from this Microsoft DevBlogs, which mainly talks about building an AI Agent on top of Copil...
Maximize Azure Cosmos DB Performance with Azure Advisor Recommendations
In the first post of this series, we introduced how Azure Advisor helps Azure Cosmos DB users uncover opportunities to optimize efficiency and...
February Patches for Azure DevOps Server
We are releasing patches for our self‑hosted product, Azure DevOps Server. We strongly recommend that all customers stay on the latest, most s...
Building AI-Powered Apps with Azure Cosmos DB and the Vercel AI SDK
The Vercel AI SDK is an open-source TypeScript toolkit that provides the core building blocks for integrating AI into any JavaScript applicati...
Time Travel in Azure SQL with Temporal Tables
Applications often need to know what data looked like before. Who changed it, when it changed, and what the previous values were. Rebuilding t...