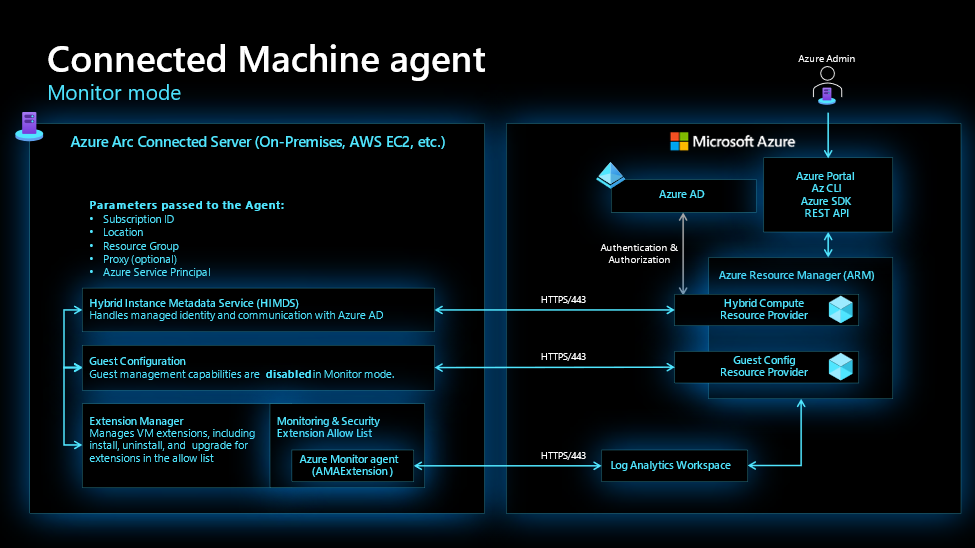
Monitor mode: Azure’s monitoring capabilities delivered securely to Azure Arc-enabled servers

Monitor mode offers a simple and scalable way for customers to configure the Connected Machine agent for monitoring and security scenarios across hybrid, multicloud, and edge environments.
Security controls provide flexibility and customization in locking down the Connected Machine agent.
While Azure Arc-enabled servers affords a robust range of capabilities delivered through extensions and Machine Configuration, some of these capabilities may not be appropriate for sensitive servers like Active Directory Domain controllers or severs handling sensitive payment data. Available from Connected Machine agent 1.16 and above, security controls provide users the flexibility to lock down the Connected Machine agent’s capabilities. For example, if you want to avoid usage of Custom Script Extension on Azure Arc-enabled servers, security controls could be used to define an allow list of extensions or block list of extensions. Alternatively, if you want to avoid configuring server settings with Machine Configuration, the Guest Configuration service can be disabled with a security control. Security controls provide flexibility to lock down the Connected Machine agent on your terms.
Monitor mode groups together a set of predefined security controls, appropriate for using Azure Arc-enabled servers in restricted monitoring and security scenarios.
Modes are pre-defined configurations of security controls, extension allow lists and guest configuration, maintained by Microsoft. Available from Connected Machine agent 1.18 and above, Monitor mode groups together the appropriate security controls to limit Connected Machine Agent capabilities to only monitoring and security scenarios. Monitor mode has disabled Machine Configuration capabilities and allows only a limited set of extensions for monitoring and security. Moreover, Monitor mode disables the configuration property for incoming connection ports, preventing capabilities like SSH Arc and Windows Admin Center (WAC), which can be used for remote management of Azure Arc-enabled servers. Note, as more monitoring and security extensions are made available, Microsoft will update the allow list and agent configuration. This list of extensions cannot be modified from Monitor Mode. To define a custom list of allowed extensions, full mode with security controls must be used. With Monitor mode, Azure Arc-enabled servers will extend OS support to Windows 10 customers for their migration from legacy Log Analytics agents (both MMA on Windows and OMS on Linux) to Azure Monitor agent (AMA). Monitor mode provides a built-in offering a streamlined approach to locking down the Connected Machine agent.
A subset of Connected Machine agent capabilities (Full mode) are available in Monitor mode.
|
Capability |
Full mode (Default) |
Monitor mode |
|
Microsoft Defender for Cloud |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Microsoft Sentinel |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Azure Monitor agent |
Allowed |
|
|
Log Analytics extension |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
VM Insights (Service Map) |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Qualys |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Custom Script Extension |
Allowed |
Not Allowed |
|
Azure Automation Update Management (v1) |
Allowed |
Allowed |
|
Update Management Center (v2) |
Allowed |
Not Allowed |
|
Hybrid Runbook Worker |
Allowed |
Not Allowed |
|
Change Tracking & Inventory Management |
Allowed |
Not Allowed |
|
Key Vault |
Allowed |
Not Allowed |
|
Machine Configuration (Guest Configuration) |
Enabled |
Disabled |
|
Connectivity to Windows Admin Center and SSH Arc |
Enabled |
Disabled |
As customers continue to leverage Azure Arc-enabled servers for extending their Azure’s observability services to their non-Azure infrastructure, Monitor mode empowers users with the control to meet the diverse security needs of their heterogeneous compute.
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Automating Business PDFs Using Azure Document Intelligence and Power Automate
In today’s data-driven enterprises, critical business information often arrives in the form of PDFs—bank statements, invoices, policy document...
Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions Enhancements, Foundry Rebranding, and Azure Pipelines Improvements
This post announces the December release of the Azure Developer CLI (`azd`). The post Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions En...
Unlock the power of distributed graph databases with JanusGraph and Azure Apache Cassandra
Connecting the Dots: How Graph Databases Drive Innovation In today’s data-rich world, organizations face challenges that go beyond simple tabl...
Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot
A few months ago we introduced the Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot in private preview. The goal was simple: allow teams to take a...
Microsoft Dataverse – Monitor batch workloads with Azure Monitor Application Insights
We are announcing the ability to monitor batch workload telemetry in Azure Monitor Application Insights for finance and operations apps in Mic...
Copilot Studio: Connect An Azure SQL Database As Knowledge
Copilot Studio can connect to an Azure SQL database and use its structured data as ... The post Copilot Studio: Connect An Azure SQL Database ...
Retirement of Global Personal Access Tokens in Azure DevOps
In the new year, we’ll be retiring the Global Personal Access Token (PAT) type in Azure DevOps. Global PATs allow users to authenticate across...
Azure Cosmos DB vNext Emulator: Query and Observability Enhancements
The Azure Cosmos DB Linux-based vNext emulator (preview) is a local version of the Azure Cosmos DB service that runs as a Docker container on ...