NetApp Cloud Volume ONTAP (CVO) for Azure – EDA Benchmark and Best Practices
Co-authors:
- Meng-Ru (Raymond) Tsai Senior Program Manager, Azure HPC+AI, Microsoft
- Tang Chao, Solutions Architect, NetApp
- Virgilio Inferido, Member of Technical Staff, NetApp
- Giancarlo DiPasquale, Azure HPC Architect, Microsoft
- Richard Paw, Director, Semiconductors & EDA, Azure Global, Microsoft.
- Jon Austin, Azure HPC Architect, Microsoft
Objective
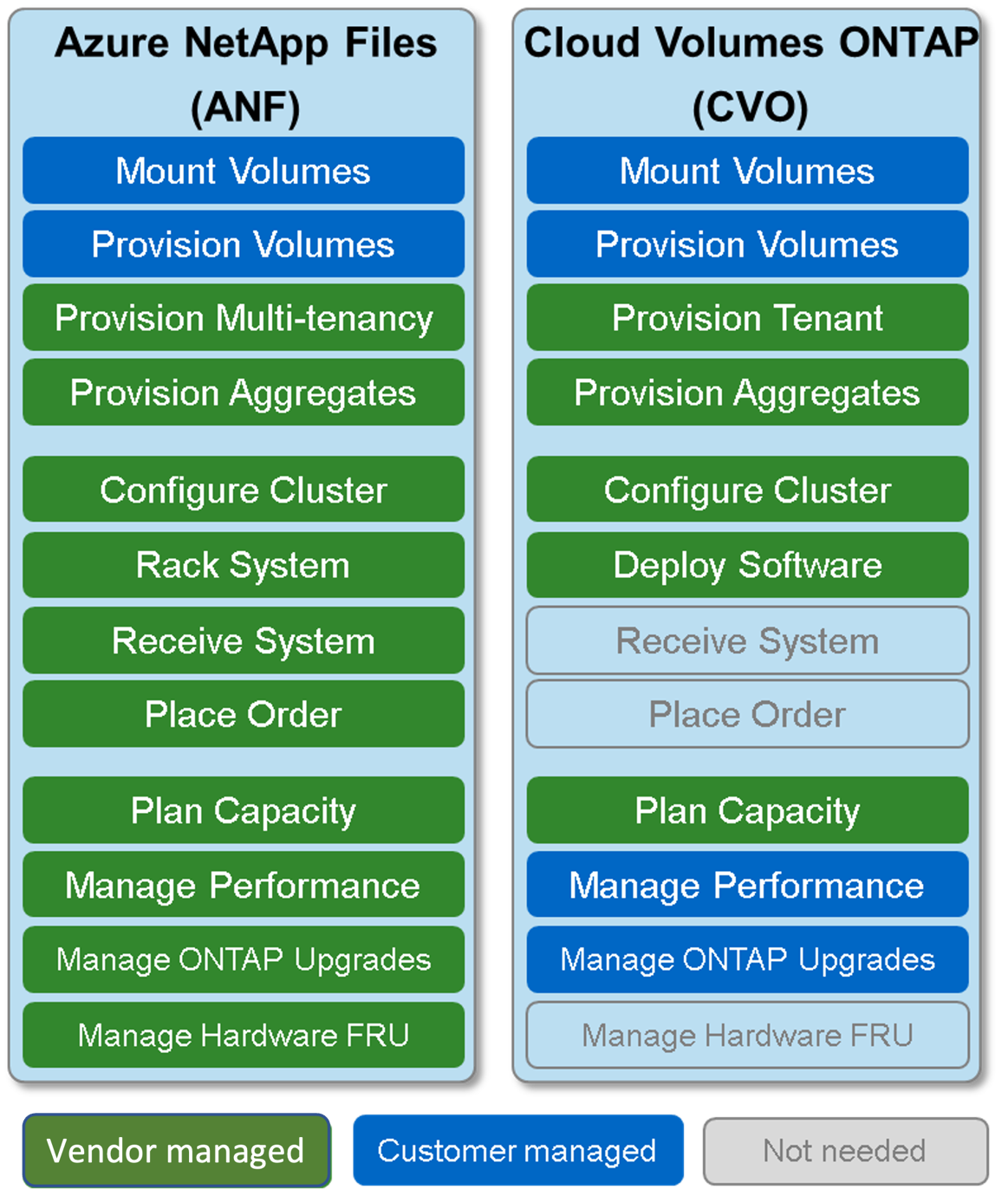
NetApp Cloud Volumes ONTAP (CVO) is a full featured ONTAP NAS solution that runs on the Azure High Performance Compute (HPC) stack. It is a complementary offering to the fully managed Azure NetApp Files, Enterprise-grade NAS.
This article provides benchmark reference and architectural guidance to customers who are considering migration of their Electronic Design Automation (EDA) workload to Azure, using CVO as the NFS solution. Furthermore, it provides guidance on where and how to best deploy CVO for EDA workloads. This article focuses on benchmark performance and does not address CVO setup or configuration.
EDA workloads are demanding, even for on-premises hardware. In the cloud, EDA workloads need the most performant storage solution possible. Our goal was to find the configuration with the best benchmark performance.
Where to use CVO
- Azure regions where Azure NetApp Files (ANF) is not available.
Note: ANF is the suggested NFS solution for running EDA workloads on Azure. ANF lets customers provision the desired size of ONTAP volumes in seconds without ONTAP administration tasks like setup, configuration, or upgrade.
- Customers using a hybrid-cloud use case where data, tools or libraries are synchronized or replicated between Azure and on-premises NetApp.
- Customers who need to integrate existing ONTAP CLI and ZAPI scripts and workflows that were built around NetApp ONTAP operating systems for compatibility reasons.
- Customers who prefer to manage their ONTAP upgrade rhythm on their own or use bring-your-own-license (BYOL) to Azure.
- Customers who use enhanced support with third-party LDAP or other authentication solutions not available with ANF.
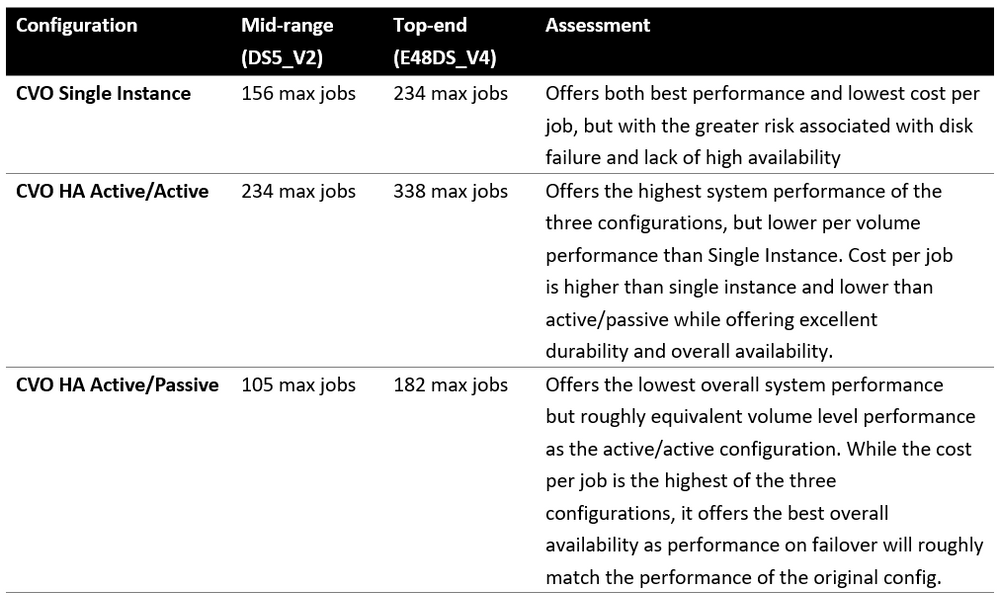
Table 1 below shows the high-level comparison between ANF and CVO, to help with the CVO and ANF selection process.
Table 1: The high-level comparison between ANF and CVO from the administrator’s point of view.
Note that storage aggregates need to be managed by customer in CVO (source: NetApp)
An industry standard benchmark was used rather than a generic IO benchmark tool like “fio” or “dd”, which generate predictable workload patterns. The tool instead provides workloads that more closely resemble those encountered in EDA to provide industry relevant results.
Azure architecture for EDA workloads
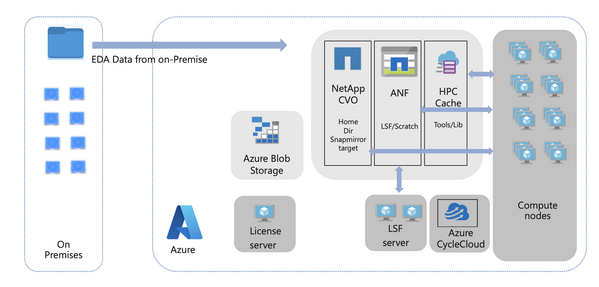
Figure 1: High-level Azure architecture for EDA workloads
Figure 1 below shows a high-level architecture diagram for running EDA workloads in Azure, which includes compute, storage, networking, and orchestration components. The area highlighted by the red rectangle indicates the NFS solution. Our experience shows that the appropriate NFS solution is critical to performance, as it needs to provide sufficient IOPS and throughput with small latency, generally < 2 milliseconds (ms) per operation, to fulfill the different requirements of EDA workloads. We will be focusing on benchmarking NetApp CVO on Azure to help construct a performant NFS storage solution. We will not be addressing ANF in this article.
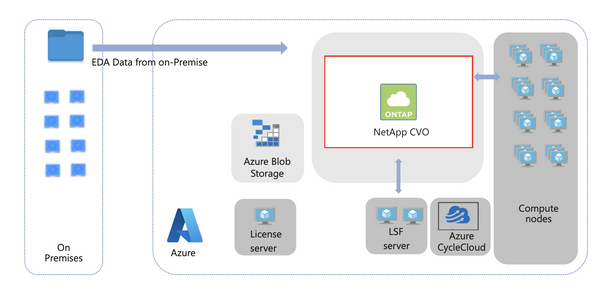
Figure 2: High-level Azure architecture for EDA workloads with CVO
Benchmarking architecture
In all tests, Cloud Volumes ONTAP 9.11.1 was used. The clients were 24 type E16ds_v4 VMs running OS RHEL 7.9. Accelerated Networking was enabled and the NFSv3 protocol was used.
Three CVO configurations were tested:
- CVO Single Instance
- CVO HA Active/Active
- CVO HA Active/Passive
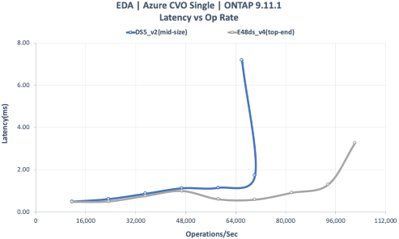
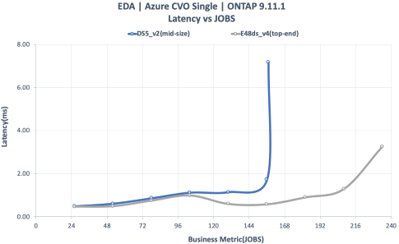
CVO Single Instance Configuration
- E48ds_v4 (top-end) | DS5_v2 (mid-range)
- One LIF
- 24TB FlexGroup (8 constituents)
- LDM (High write speed) Enabled
- SIDL (Single Instance Data Logging) Off
- Twelve Premium SSD aggregate at 2TB size per disk
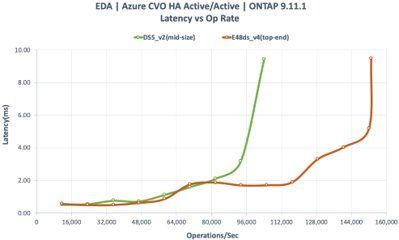
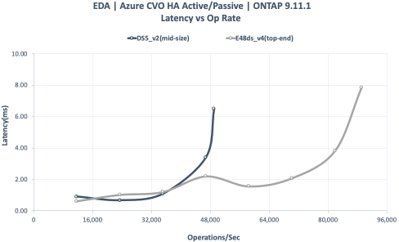
CVO HA Active/Active Configuration
- E48ds_v4 (top-end) | DS5_v2 (mid-range)
- Two LIFs
- 48TB FlexGroup (8 constituents) per node
- LDM (High write speed) Enabled
- SIDL (Single Instance Data Logging) Off
- Twelve Premium SSD aggregate at 2TB size per disk
CVO HA Active/Passive Configuration
- E48ds_v4 (top-end) | DS5_v2 (mid-range)
- One LIF
- 24TB FlexGroup (8 constituents)
- LDM (High write speed) Enabled
- SIDL (Single Instance Data Logging) Off
- Twelve Premium SSD aggregate at 2TB size per disk
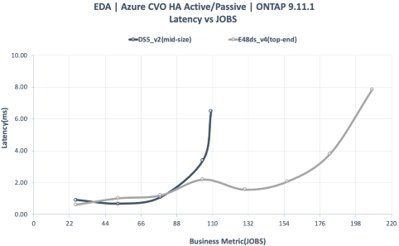
Cost/Performance Assessment
Table 2: Assessment of three CVO for Azure configurations for EDA workloads
NetApp Cloud Volume ONTAP (CVO) on Azure provides semiconductor customers with alternatives for NFS operations where Azure NetApp Files (ANF) is not available in the region or ONTAP features are required, i.e. FlexCache, CLI, ZAPI, etc., when high performance NFS storage is needed for EDA workloads.
Additional Resources
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Microsoft Power BI: Tenant setting changes for Microsoft Azure Maps in Power BI
Admins will have updated tenant settings for Azure Maps in Power BI, split into three controls. The update requires Power BI Desktop April 202...
Build 2025 Preview: Transform Your AI Apps and Agents with Azure Cosmos DB
Microsoft Build is less than a week away, and the Azure Cosmos DB team will be out in force to showcase the newest features and capabilities f...
Fabric Mirroring for Azure Cosmos DB: Public Preview Refresh Now Live with New Features
We’re thrilled to announce the latest refresh of Fabric Mirroring for Azure Cosmos DB, now available with several powerful new features that e...
Power Platform – Use Azure Key Vault secrets with environment variables
We are announcing the ability to use Azure Key Vault secrets with environment variables in Power Platform. This feature will reach general ava...
Validating Azure Key Vault Access Securely in Fabric Notebooks
Working with sensitive data in Microsoft Fabric requires careful handling of secrets, especially when collaborating externally. In a recent cu...