Optimize Azure Kubernetes Service Node Cost by Combining OnDemand And Spot VMs
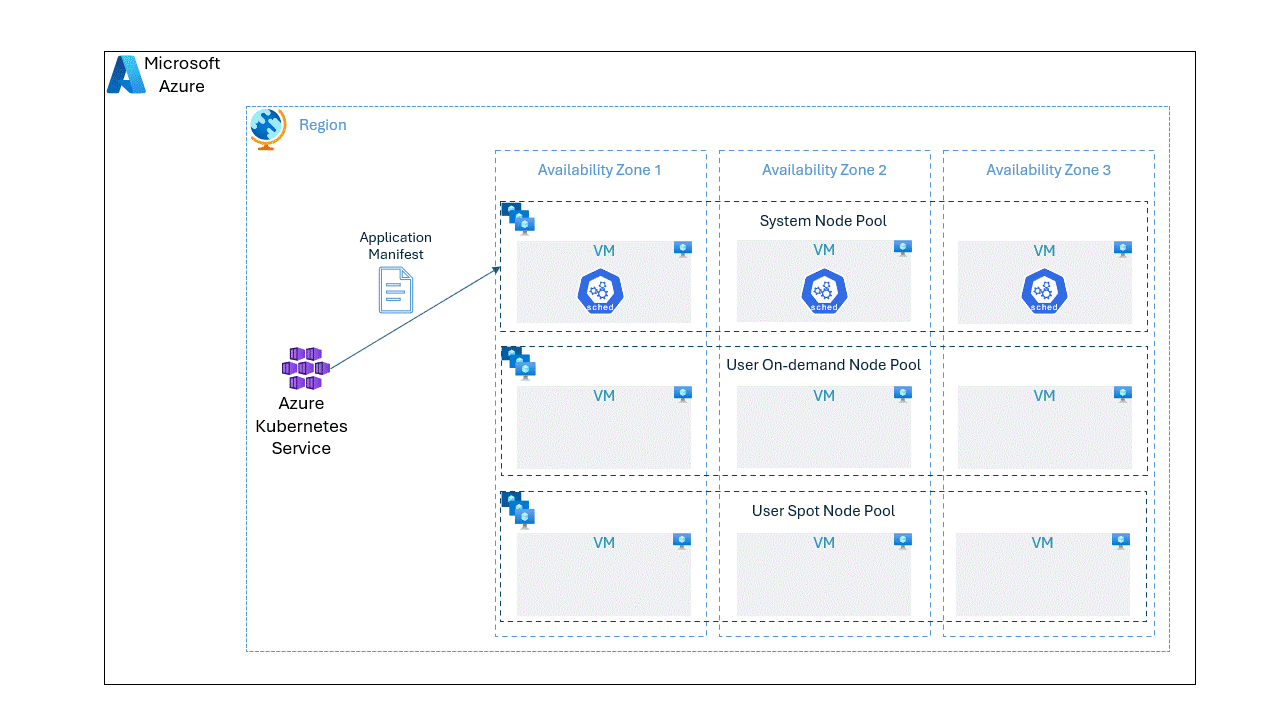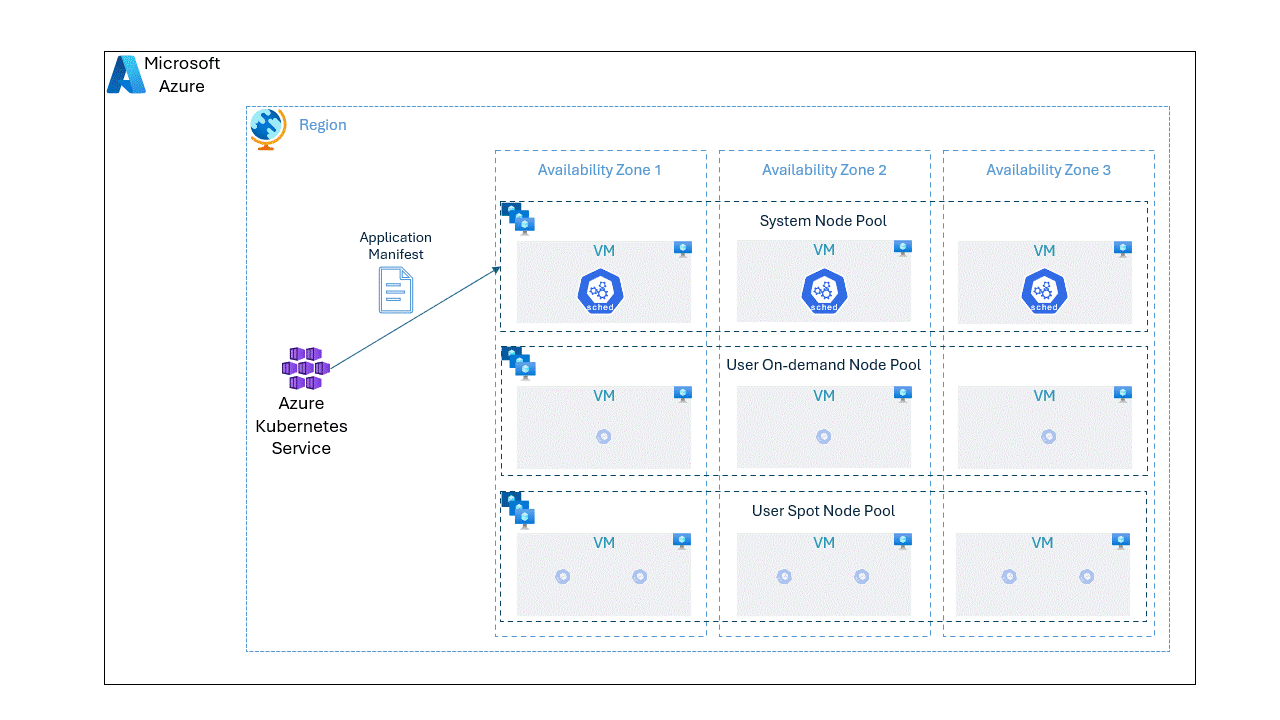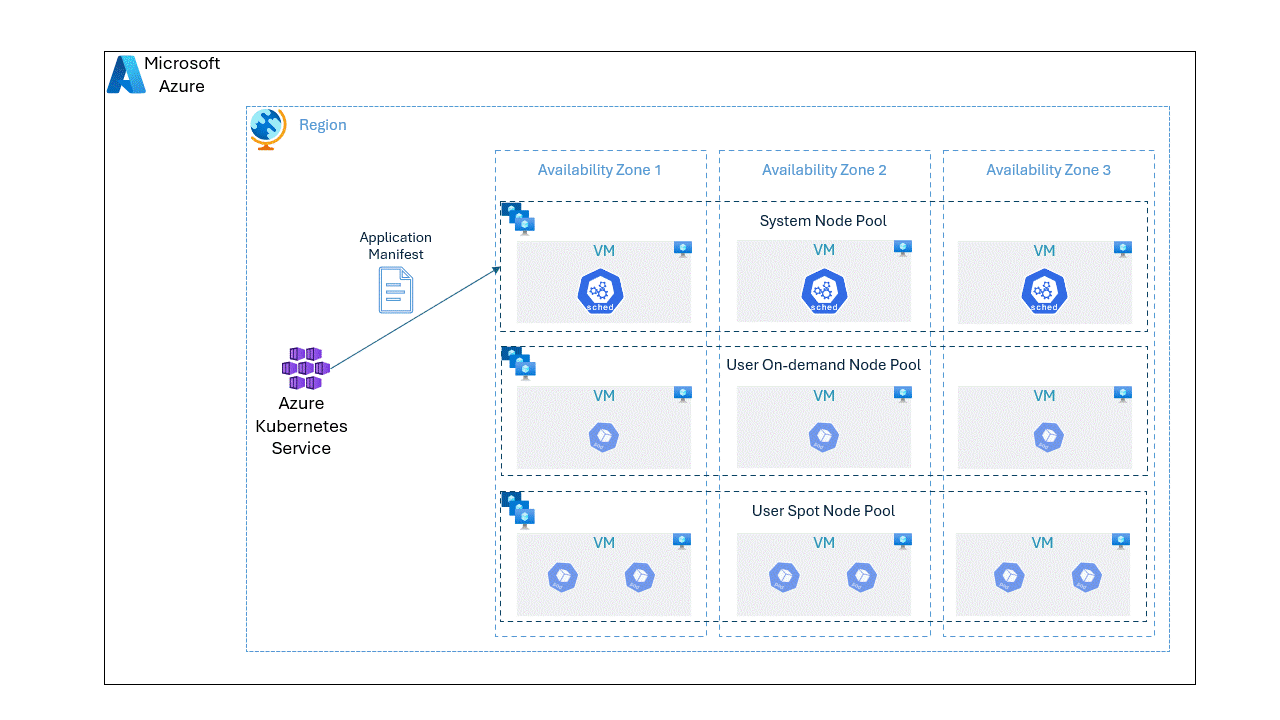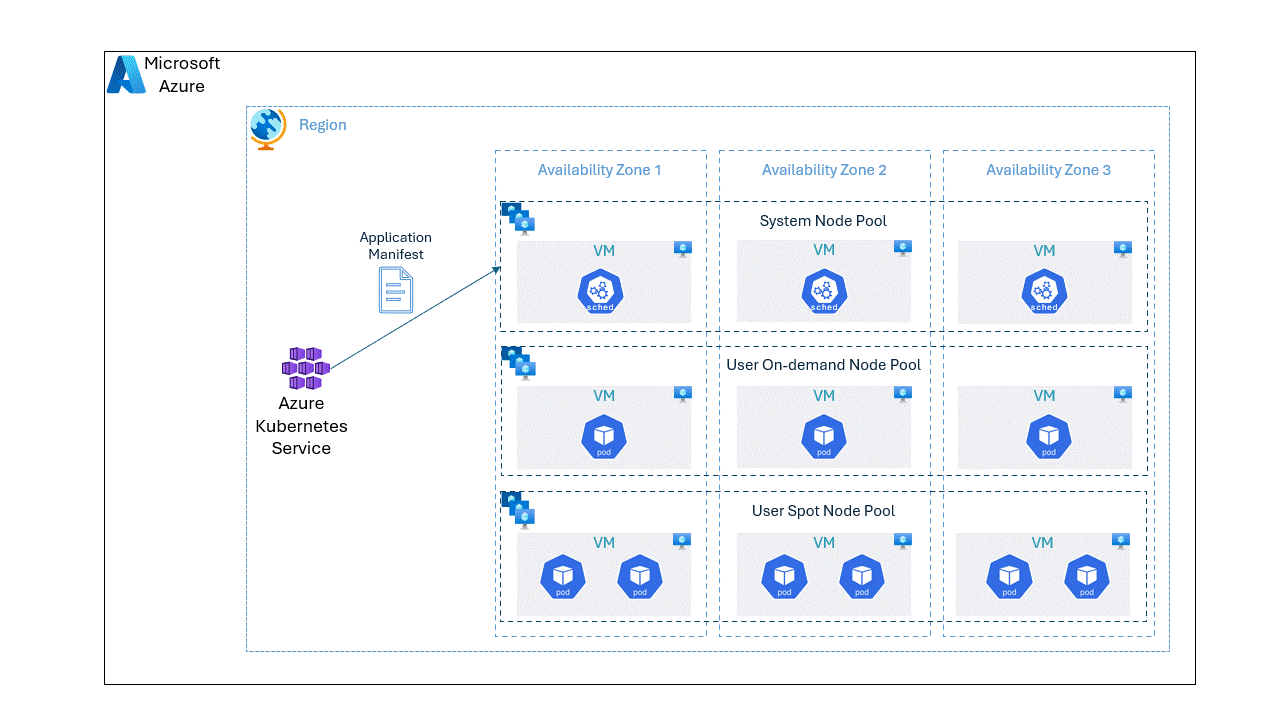
While it's possible to run the Kubernetes nodes either in on-demand or spot node pools separately, we can optimize the application cost without compromising the reliability by placing the pods unevenly on spot and OnDemand VMs using the topology spread constraints. With baseline amount of pods deployed in OnDemand node pool offering reliability, we can scale on spot node pool based on the load at a lower cost.
In this post, we will go through a step by step approach on deploying an application spread unevenly on spot and OnDemand VMs.
Prerequisites
- Azure Subscription with permissions to create the required resources
- Azure CLI
- kubectl CLI
1. Create a Resource Group and an AKS Cluster
Create a resource group in your preferred Azure location using Azure CLI as shown below
Let's create an AKS cluster using one of the following commands.
OR
2. Create two node pools using spot and OnDemand VMs
3. Deploy a sample application
4. Update the application deployment using topology spread constraints
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution we ensure that the pods are placed in nodes which has deploy as key and the value as either spot or ondemand. Whereas for preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution we will add weight such that spot nodes has more preference over OnDemand nodes for the pod placement.topologySpreadConstraints with two label selectors. One with deploy label as topology key, the attribute maxSkew as 3 and DoNotSchedule for whenUnsatisfiable which ensures that not less than 3 instances (as we use 9 replicas) will be in single topology domain (in our case spot and ondemand). As the nodes with spot as value for deploy label has the higher weight preference in node affinity, scheduler will most likely will place more pods on spot than OnDemand node pool. For the second label selector we use topology.kubernetes.io/zone as the topology key to evenly distribute the pods across availability zones, as we use ScheduleAnyway for whenUnsatisfiable scheduler won't enforce this distribution but attempt to make it if possible.Conclusion
maxSkew configuration in topology spread constraints is the maximum skew allowed as the name suggests, so it's not guaranteed that the maximum number of pods will be in a single topology domain. However, this approach is a good starting point to achieve optimal placement of pods in a cluster with multiple node pools.Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Semantic Reranking with Azure SQL, SQL Server 2025 and Cohere Rerank models
Supporting re‑ranking has been one of the most common requests lately. While not always essential, it can be a valuable addition to a solution...
How Azure Cosmos DB Powers ARM’s Federated Future: Scaling for the Next Billion Requests
The Cloud at Hyperscale: ARM’s Mission and Growth Azure Resource Manager (ARM) is the backbone of Azure’s resource provisioning and management...
Automating Business PDFs Using Azure Document Intelligence and Power Automate
In today’s data-driven enterprises, critical business information often arrives in the form of PDFs—bank statements, invoices, policy document...
Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions Enhancements, Foundry Rebranding, and Azure Pipelines Improvements
This post announces the December release of the Azure Developer CLI (`azd`). The post Azure Developer CLI (azd) Dec 2025 – Extensions En...
Unlock the power of distributed graph databases with JanusGraph and Azure Apache Cassandra
Connecting the Dots: How Graph Databases Drive Innovation In today’s data-rich world, organizations face challenges that go beyond simple tabl...
Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot
A few months ago we introduced the Azure Boards integration with GitHub Copilot in private preview. The goal was simple: allow teams to take a...
Microsoft Dataverse – Monitor batch workloads with Azure Monitor Application Insights
We are announcing the ability to monitor batch workload telemetry in Azure Monitor Application Insights for finance and operations apps in Mic...
Copilot Studio: Connect An Azure SQL Database As Knowledge
Copilot Studio can connect to an Azure SQL database and use its structured data as ... The post Copilot Studio: Connect An Azure SQL Database ...
Retirement of Global Personal Access Tokens in Azure DevOps
In the new year, we’ll be retiring the Global Personal Access Token (PAT) type in Azure DevOps. Global PATs allow users to authenticate across...