Introducing Azure Key Vault and Managed HSM Engine: An Open-Source Project

Azure Key Vault and Managed HSM Engine allows OpenSSL-based applications to use RSA/EC private keys protected by Azure Key Vault and Managed HSM. It leverages the OpenSSL engine interface to perform cryptographic operations inside Azure Key Vault and Managed HSM. The goal is to seamlessly onboard OpenSSL-based applications to these services.
High-Level Design
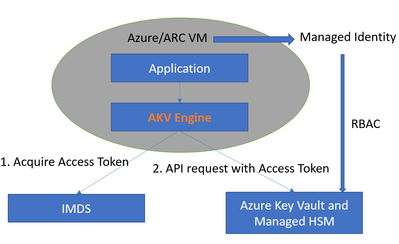
At a high level, the workflow is described in the diagram below.
The workflow has two parts:
1. Key Management
The security admin creates the Azure Key Vault or Managed HSM resource, then provisions keys in it. The security admin also manages access to the keys via RBAC (Role-Based Access Control). In this workflow, the application will be deployed to an Azure VM or ARC VM. The VM will be assigned a managed system identity, and the security admin grants access to the key by assigning appropriate Azure roles to the managed system identity.
2. Application
The application code will use the OpenSSL library for cryptographic operations and specify the key to be used via an engine private key string. Under the hood, cryptographic operations are performed by the engine. The engine will first acquire the access token from Azure IMDS and then parse the engine private key string to generate the RESTful API URL and convert the cryptographic operation to a RESTful API call. After the remote Azure Key Vault or Managed HSM finishes the cryptographic operation and returns the result, the engine will convert the result and return it back to the application.
The engine private key string contains five sections separated by semicolons:
engine:e_akv:[Key Vault type]:[Azure Key Vault or HSM name]:[key name]
- The first section engine is reserved and should NOT be changed.
- The second section is for the engine name. e_akv stands for “engine for Azure Key Vault.”
- The third section is for the type of Azure Key Vault. There are two types: “vault” and “managedHsm.” If the key is stored in Azure Key Vault, then the value will be “vault.” If the key is stored in managed HSM, the value will be “managedHsm.” They are case-insensitive.
- The fourth section is for the name of the Azure key vault or managed HSM which is created by the security admin.
- The fifth section is the key’s name.
The value from the third, fourth, and fifth sections will be used to generate the restful API URL to access the Azure Key Vault or Managed HSM.
For example, the engine string
engine:e_akv:managedHsm:myHsm:myKey
will generate the RESTful API URL
https://myHsm.managedhsm.azure.net/keys/myKey
Stay tuned for future posts, where we can explore additional integrations and extensions of this project. The team welcomes contributions to the projects via the Microsoft Open Source Github.
Published on:
Learn moreRelated posts
Azure Developer CLI (azd): One command to swap Azure App Service slots
The new azd appservice swap command makes deployment slot swaps fast and intuitive. The post Azure Developer CLI (azd): One command to swap Az...